Location: Home > Research News
Research News
Researchers print high-performance microcone-array flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor
According to the data of the World Health Organization, about 430 million people worldwide suffer from hearing loss due to cochlear damage, and the improvement of hearing mainly depends on cochlear implants. However, traditional cochlear implants have low speech recognition ability, and the mismatch between rigid electrodes and soft tissues may lead to nerve damage and tinnitus. With the development of Internet of Things and artificial intelligence, the research of flexible self-powered cochlear implants has attracted extensive attention.
Recently, Prof. SONG Yanlin and Associate Prof. Lihong Li from the Institute of Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences (ICCAS), inspired by human outer ear hair cells, developed a novel strategy of a highly efficient and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor (FPAS) with microcone patterning arrays based on multicomponent lead-free perovskite rod niobate piezoelectric materials with the morphotropic phase boundary. The output voltage of the rod-based FPAS is nearly 300% of that of the isotropic particles. The microcone patterning FPAS with stable performance in harsh environments shows high sensitivity (39.22 mV?Pa-1?cm-2) due to the significant enhancement of sound energy absorption and can record sound signals, recognize audio signals and realize human-computer interaction.
Furthermore, this work demonstrates that the FPAS holds promise for various applications, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cochlea implants, wearable acoustic equipment, and human-computer interaction. This research work has been recently published in Matter.
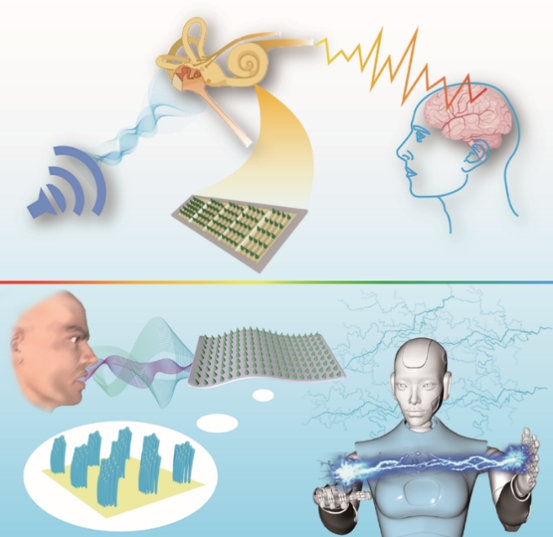
Figure 1 The flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor (FPAS) with cone arrays mimicking outer ear hair cells (Image by XIANG Zhongyuan)
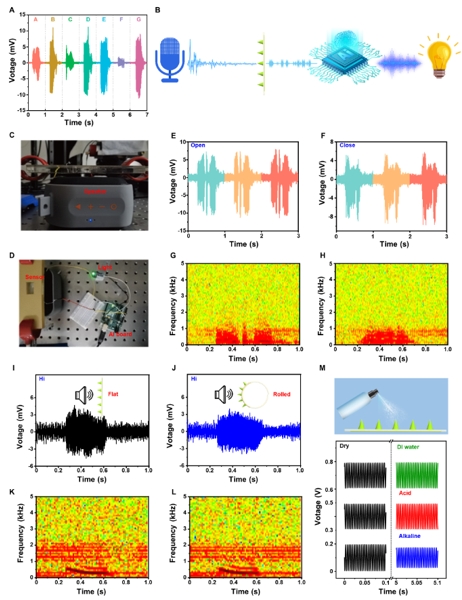
Figure 2 Human-computer interaction applications and waterproofing of the flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor (Image by XIANG Zhongyuan)
Contact:
Prof. SONG Yanlin or LI Lihong
Email: ylsong@iccas.ac.cn or lilihong1209@iccas.ac.cn





