Cobalt Nanoskeletons: One-Pot Solution Synthesis of Cubic Cobalt Nanoskeletons
In recent years, nanostructured materials with hollow interiors have attracted increasing interest because of their specific structures, interesting properties that differ from their solid counterparts, and wide applications in chemistry, biotechnology, and materials science. In particular, diverse single-crystalline or single-crystalline like hollow metal polyhedra have been investigated extensively due to their unique physical and chemical characteristics. As an important magnetic metal material, nanosized Co crystals have extensive applications in heterogeneous catalysis, sensors and ultra-high-density magnetic recording.
Multi-steps were generally needed in the synthesis of hollow structured materials. By the introduction of the etchant into the in-situ reduction process, cubic Co nanoskelectons via one-pot solution route were successfully synthesized. The in-situ reduction, Ostwald ripening and facet-selective coordination-assisted etching seem to be responsible for the formation of these novel structures. Furthermore, the above processes can be well controlled by simply controlling the reaction time, thus cubic Co nanoaggregates, nanocages, and nanoskelectons can be easily prepared. These nanoskelectons exhibited superior magnetic properties(such as enhanced HC) compared with the solid cube-like aggregates and nanocages due to the increase of shape anisotropy.This work may provide a possible and easy way to controllable synthesis of hollow metal nanopolyhedra by the introducing an appropriate etchant into the synthesis process.
Advanced Materials,2009, 21, 1636-1640
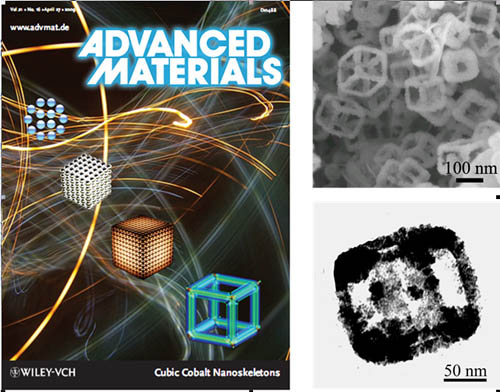
Cover picture (Adv. Mater. 16/2009), SEM and TEM images of Co Nanoskelectons





