Organic nano-photonics, involving the study of the behaviors of photons in organic materials at nanometer scale, has drawn increasing attention during the past couple of years. The organic single crystals with the superior optical/electrical properties are promising candidate in future optoelectrics. Prof. Yao Jiannian and Prof. Zhao Yong Sheng’s groups in the the Chinese Academy of Sciences(CAS) Key Laboratory of Photochemistry, in the Institute of Chemistry, the Chinese Academy of Sciences(ICCAS) have studied on the fabrication of organic optical waveguides and organic nanowire lasers (Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 1661-1665; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7301-7305) in their previous works. They also found the mechanism of Exciton polariton (EP) in organic photonic processes, and realized stable white light outcoupling by doping a kind of triplet sensitizer into organic nanowire waveguides (Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 1380-1384). After that, they also obtained two-photon pumped organic nanowire lasers via the high refraction index of EPs. (J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2011,133, 7276–7279).
Recently, under the supports from the National Nature Science Foundation of China , the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and ICCAS, they developed a two step process for the construction of dendritic organic heterojunctions in collaboration with Professor Huang Jiaxing in Northwestern University, USA. The tree-like structures emit various wavelengths of light when excited by a focused laser beam, and could be useful for the development of circuits for photonic computing and information processing. The results have been published in J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2012,134, 2880-2883.
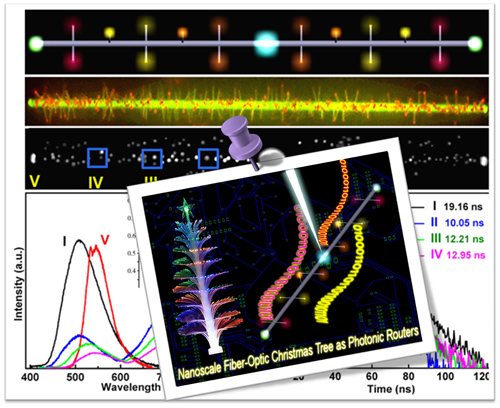
Figure 1. Low-dimensional organic photonic routers, in which different photonic signals can be output from various channels with a single input. (Image by Zheng Jianyao and Yan Yongli)
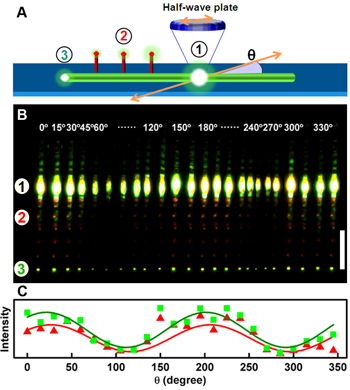
Figure 2. Modulation of the output signals from the photonic routers by the polarization of excitation. (Image by Zheng Jianyao and Yan Yongli)
