By Heng-Xing Ji Jin-Song Hu Yu-Guo Guo* Wei-Guo Song and Li-Jun Wan*
We report the design of a spatially confined system to investigate the formation of CuTCNQ. An anodized aluminum oxide (AAO) template with a well-defined close-packed pore channel array has been used as a microreactor. A well-defined CuTCNQ nanowire array with a high length/diameter ratio and a single-crystalline nature with a-axis parallel to the nanowire has been observed to form even though TCNQ molecules do not directly contact the Cu substrate (Fig. 1ab). It is amazing that Cu ions can pass through the solid complex crystal at a high rate with facile long-range transfer. From the experimental results a novel ion-transfer-based growth mechanism is proposed for the first time based on the spatial confinement of the reaction and growth processes using the AAO template (Fig. 1c). The new mechanistic understanding may provide new insights into metal-TCNQ charge-transfer complexes for further applications in organic electronics and solid state ionics.
Advanced Materials 2008 20(24) 4879-4882
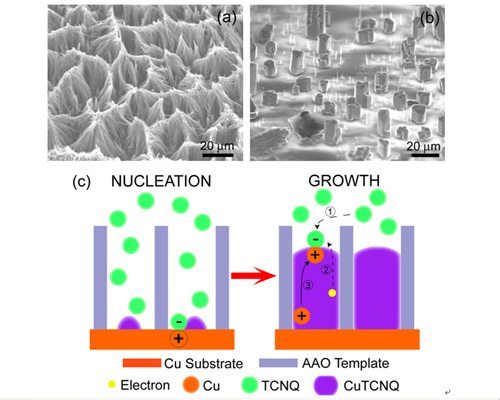
(a) SEM images of CuTCNQ nanowire arrays after removal of the AAO template; (b) Tilted-view SEM image of CuTCNQ bulk crystal arrays standing upright on AAO templates; (c) Schematic illustration of the formation process of CuTCNQ nanowires.
,
