| |
Yanli Shang, Yongqiang Wen,* Shaolu Li, Shixuan Du, Xiaobo He, Li Cai, Yingfeng Li, Lianming Yang, Hongjun Gao, and Yanlin Song*
A triphenylamine-containing donor-acceptor molecule, 2-((Z)-2-(4-diphenylamino)
benzylidene)-1,2-dihydro-1-oxoinden-3-ylidene) malononitrile (BDYOM) was designed and synthesized for rewritable data storage. The triphenylamine unit can improve the intrinsic storage performance because it can not only act as a strong electron donor in its initial state but also stabilize the charge transferred state. The results showed that the thin film had excellent bistable electronic switching behavior with a high ON/OFF current ratio (Figure 1). Reversible data storage was successfully demonstrated on the thin film by STM (Figure 2). Mechanism analysis indicated that the recording dot was due to the intermolecular charge transfer induced by electric field.
J. AM. CHEM. SOC. (2007, 129, 11674-11675)
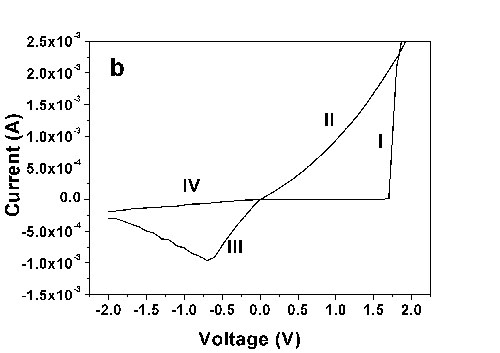
Figure 1. Macroscopic I-V characteristics of the BDOYM thin film
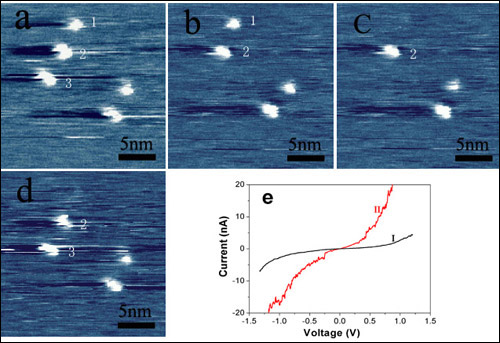
Figure 2. STM images of typical information dots pattern on the BDYOM thin film and the corresponding I-V curves. (a) Recording pattern composed of five information dots: pulsed voltage, +2.3 V; 3.0 ms. (b, c) Erasing the first and the second dots at position 1 and 3, respectively: pulsed voltage, -1.4 V; 3.0 ms. (d) Rewriting one information dot at position 1: pulsed voltage, +2.3 V; 3.0 ms. (e) Typical STM I-V curves in the unrecorded (curve I) and recorded region (curve II).
, |
|
