Chong-an Di Gui Yu* Yunqi Liu* Xinjun Xu Dacheng Wei Yabin Song Yanming Sun Ying Wang Daoben Zhu* Jian Liu Xinyu Liu and Dexin Wu
The characteristics of organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) were dramatically improved by chemically modifying the surface of the bottom-contact Ag or Cu source-drain (D-S) electrodes with a simple solution method. The contact resistance and energetic mismatch typically observed with Ag D-S electrodes in pentacene bottom-contact OFETs can be properly eliminated when modified by the Ag-TCNQ (TCNQ ) 7788-tetracyanoquinodimethane). The pentacene transistors with low-cost Ag-TCNQ-modified Ag bottom-contact electrodes exhibit outstanding electrical properties which are comparable with that of the Au top-contact devices. It thus provides a novel way toward high-performance low-cost bottom-contact OFETs.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2006 Vol. 128 No. 51 16418-16419)
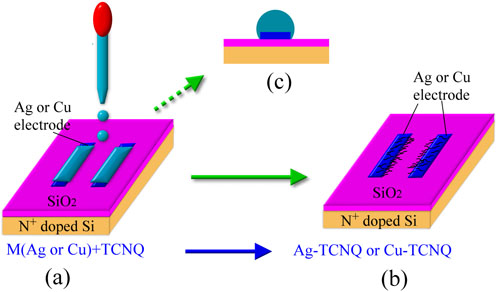
Figure 1. Schematic illustration for modification of the Ag (or Cu) electrodes by Ag-TCNQ (or Cu-TCNQ). (a) Dropping TCNQ solution in acetonitrile onto the OTS-modified SiO2 with the bottom patterned Ag or Cu source-drain electrodes. (b) The modified source-drain electrode. (c) The TCNQ solution is aggregated on the Ag or Cu surfaces due to hydrophobicity of the OTS-modified SiO2 surfaces.
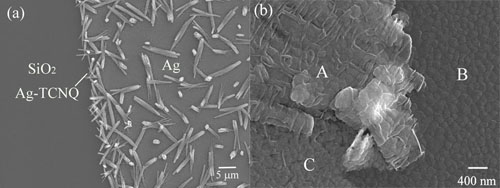
Figure 2. SEM images of (a) the Ag-TCNQ modified Ag electrodes and (b) pentacene deposited on the surface of (A) Ag-TCNQ (B) SiO2 and (C) Ag.
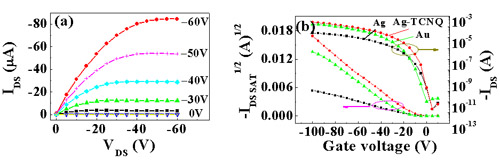
Figure 3. Output characteristics of the pentacene bottom-contact OFETs: (a) with the Ag-TCNQ modified Ag S-D electrodes; (b) Transfer characteristics of the transistor based on pentacene with different electrodes (■) the Ag bottom-contact electrode (●)Ag-TCNQ/Ag bottom-contact electrode and (▲)Au top contact electrode. , |
