Kai Xiao Yunqi Liu* Ting Qi Wei Zhang Fang Wang Jianhua Gao Wenfeng Qiu Yongqiang Ma Guanglei Cui Shiyan Chen Xiaowei Zhan Gui Yu Jingui Qin* Wenping Hu and Daoben Zhu*
We present the synthesis and characterization of a fused-ring compound dithieno[23-d:2ˇ3ˇ-dˇ]thieno[32- b:45-bˇ]dithiophene (pentathienoacene PTA Fig. 1). In contrast to pentacene PTA has a larger band gap than most semiconductors used in organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and therefore is expected to be stable in air. The large p-conjugated and planar molecular structure of PTA would also form higher molecular orders that are conductive for carrier transport. X-ray diffraction and atomic force microscopy experiments on its films show that the molecules stack in layers with their long axis upright from the surface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy suggests that there are no chemical bonds at the PTA/Au interface. OFETs based on the PTA have been constructed (Fig. 2) and their performances as p-type semiconductors are also presented. A high mobility of 0.045 cm2/Vs and an on/off ratio of 103 for a PTA OFET have been achieved demonstrating the potential of PTA for application in future organic electronics.
J. AM. CHEM. SOC. 2005 127 13281-13286
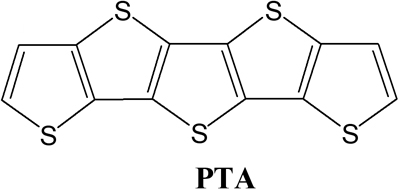
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of PTA
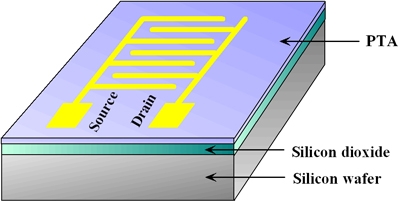
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of OFET , |
