Progress of Chemical Modification on Fullerene Cage
The unique 3D geometry of fullerenes with carbon spheres containing abundant highly reactive double bonds constitutes a rather rich scenario where a variety of different chemical reactions can occur. These chemical modifications on fullerene cage are preferred way to tune the physical and chemical properties of hollow fullerenes and endohedral fullerenes. Here we introduce two achievements in chemical modification researches on fullerene C70 and endohedral metalfullerene Sc3C2@C80.
Carbene Is Finally Attached to the Equator of C70 – the Production of the Most Stable C71H2 Isomer: 2aH-2(12)a-Homo(C70-D5h(6))[5,6]fullerene
Bao Li, Chunying Shu*, Xin Lu*, Lothar Dunsch, Zhongfang Chen, T. John S. Dennis, Zhiqiang Shi, Li Jiang, Taishan Wang, Wei Xu, Chunru Wang*
Herein we report the synthesis, characterization, and theoretical studies of the missing C71H2 isomer-a homofullerene with a CH2 group attached to the C70 equator. The production and characterization of the thermodynamically most stable but kinetically unfavorable C71H2 isomer, together with the systematic theoretical studies, not only offer us direct experimental evidence in answer to some important chemical questions, such as the local aromaticity of C70 and the structure of divalent-group adducts of normal diameter single-walled nanotubes, but also introduce a new member into the homofullerene family and provide a new route for the synthesis of novel stable fullerene derivatives that can not be obtained under routine synthetic conditions. Moreover, the pyrogenic synthesis proved to be a highly efficient approach to overcome the high activation barriers to the formation of the thermodynamically most stable isomers. More studies on this homofullerene and related systems are in progress.
Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 962-966.

Optimized structure of C70CH2-C2v.
Spin Divergence Induced by Exohedral Modification: EPR Study of Sc3C2@C80 Fulleropyrrolidine
T. S. Wang, J. Y. Wu, W. Xu, J. F. Xiang,X. Lu,B. Li, L. Jiang, C. Y. Shu,* C. R. Wang*
In this communication, we report the spin divergence in Sc3C2@C80 fulleropyrrolidine induced by exohedral modification by the Prato reaction. The 5,6-ring junction was determined to be the reaction site for the Sc3C2@C80 fulleropyrrolidine monoadduct, and the endohedral Sc3C2 cluster was deformed by the pyrrolidine addend. Most importantly, the pyrrolidine addend changes the spin density distributions and alters the paramagnetic properties of Sc3C2@C80 fulleropyrrolidine as a result. The dynamics of Sc3C2 endocluster were also discussed to elucidate the variable properties caused by the exohedral addend. Such controllable molecular paramagnetism is of great significance to the construction of novel molecular devices.
Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1786 –1789.
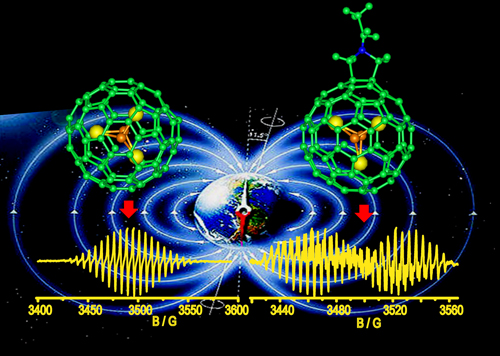
Optimized structures and ESR spectra of Sc3C2@C80 and its derivative.





